We are excited to present Siren Platform version 12 – a major release that pushes the envelope of Investigative Intelligence software.
Introducing global search
Searching data is one of the most fundamental actions of an investigator. In support of this, Siren Platform 12 commits to the search for key data by adding a new system-wide search engine – the Global Search interface.
The Global Search interface is a gateway to the new and improved record view, which is now capable of record-to-record navigation from the Linked tab.
Take a look at these features in action in this short feature video:
Autonomy for analysts
Analysts can now modify the data in dashboards and graphs, either to fix incorrect data or to create hypotheses and new scenarios. Their work can then be saved and shared with other analysts in the same dataspace.
In addition, a new contextual function is available in the Graph Browser, which allows analysts to add or edit links between nodes in the graph. This gives a new freedom of graph curation, particularly for investigations where analysts are aware of connections between entities that are not displayed.
To understand how these enhancements come together, take a look at this short feature video:
Further flexibility has also been added to our visualizations. Analysts can either switch the data set that is linked to a visualization, or can set a visualization to automatically use the entity table associated with the current dashboard. This helps to avoid the duplication of visualizations for similar searches.
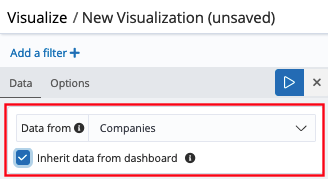
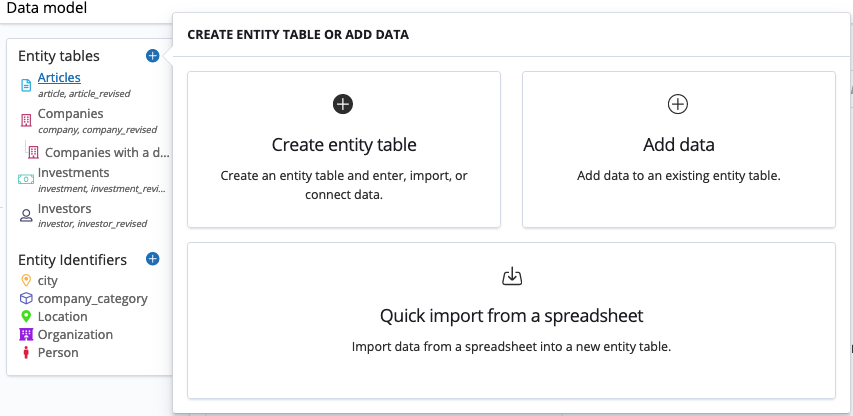
For advanced analysts, importing data and creating entity tables is part of the freedom that Siren 12 delivers.
The Data model app now provides several options for importing data, either into an existing entity table or into a new one, from spreadsheets or JDBC datasources.
Data transformation and schema editing
Yet another major new feature in Siren 12 is the ability to transform data while importing it.
The transform screen allows users to drag and drop fields and to write expressions in Painless scripting language, so that the data that is imported is in its most useful format for the investigation.
Watch this in action in this short feature video:
Graph simplicity: Nodes to edges
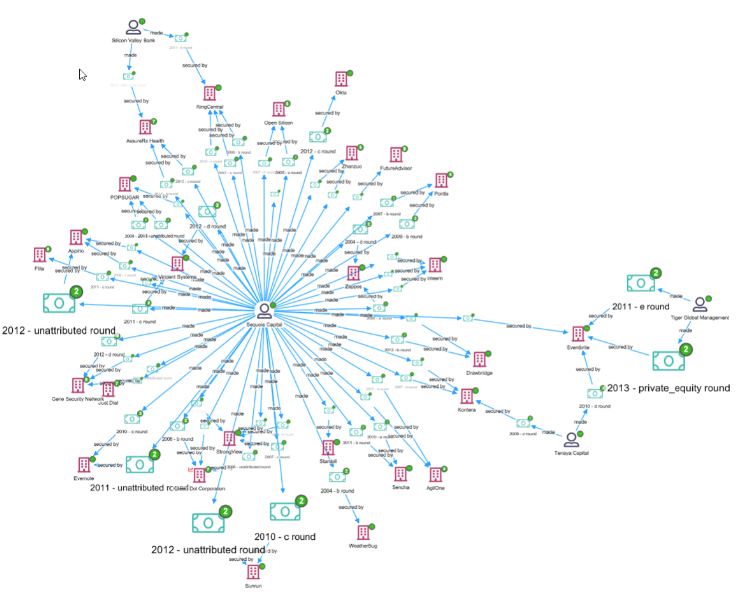
By default, Siren Investigate represents every record as a node in the graph. However, this approach can occasionally have the shortcoming of having too many nodes in the graph at once.
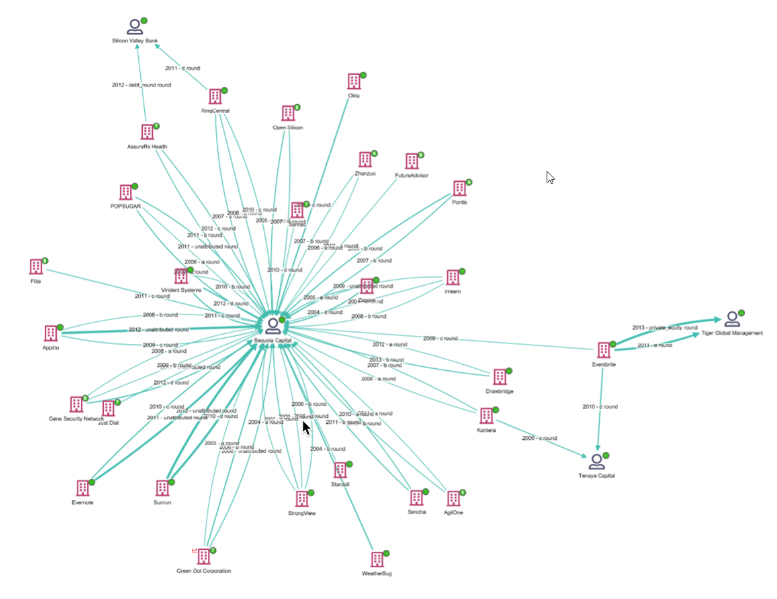
To improve graph readability, Siren 12 introduces a new graph lens that is capable of quickly changing nodes into edges (or links). For example, a financial transaction is often best visualized as a link rather than as a node itself.
If we activate the lens while viewing investor-investment-company relationships, a graph that looks like this:
Becomes noticeably simpler after the lens is applied:
Improvements to the Siren API
Using the internal Siren API, it is now possible to render React components and programmatically navigate from dashboard to dashboard. For more information, check out our scripting API documentation.
Siren Search UI
Now with security enabled
In Siren Platform version 11.1, we introduced the Siren Search UI; Siren’s mobile-friendly interface that democratizes associative search and navigation capabilities for mobile users, giving them a familiar search engine experience.
With version 12, the Search UI now uses the same security configuration as Siren Investigate, making it a breeze to deploy if Siren Investigate is already installed.
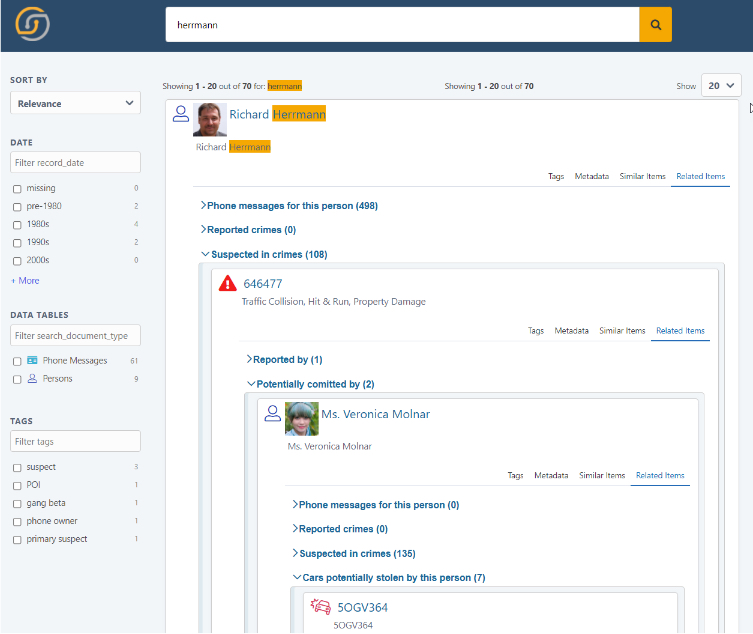
Advanced taxonomy data browsing
For customers dealing with advanced textual content, such as technical or scientific news or documentation, Siren now has the ability to perform deep taxonomy tagging and browsing.
On the tagging side, the built-in Siren NLP component can now take deep taxonomies as input, specifically:
- Taxonomies with over tens of thousands of terms
- Synonyms at every level
- Terms that have multiple roots
Next, we have added a new feature to the Controls visualization, called the Options Tree, which can be used for browsing data annotated by the NLP plugin or by others using the same convention.
As a side note, hierarchical tagging works by encoding the path, for example, /vehicle/car/midsize car, so the component not only works with data annotated by NLP, but also as a general browser of files in folders.
The trees are built using Elasticsearch aggregations on the data in your index so big data is no problem.
In this example, patent documents are filtered to view any inorganic oxide and any aircraft propulsion component. We find that the first document mentions metal oxide, an inorganic oxide, and propellant tank, an aircraft propulsion component.
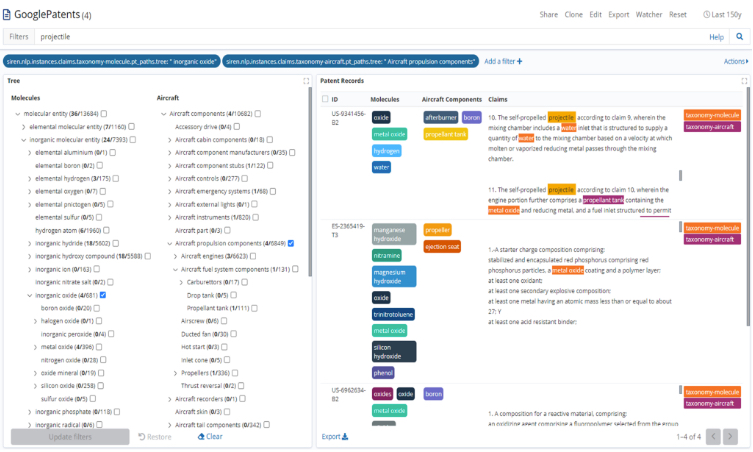
Elasticsearch transforms and outlier detection
Picture an investigation in which the analyst zones in on 100 individual companies or people and there is no clear indication of which one to investigate first.
For scenarios like this, AI comes in handy to help analysts prioritize their efforts and focus their attention.
As an extra addition to the Siren v12 release, we are making available a set of scripts and recipes to determine which entities “stand out” from others and why – exclusively for customers who use the premium Elasticsearch Platinum features (available with Siren Platform Platinum Edition).
The details of the methodology will be published soon in a dedicated blog post, but it works by leveraging the UI-driven procedures that are in Kibana to run AI outlier detection and to enrich existing records with outlier scores.
Watch it in action in this short video:
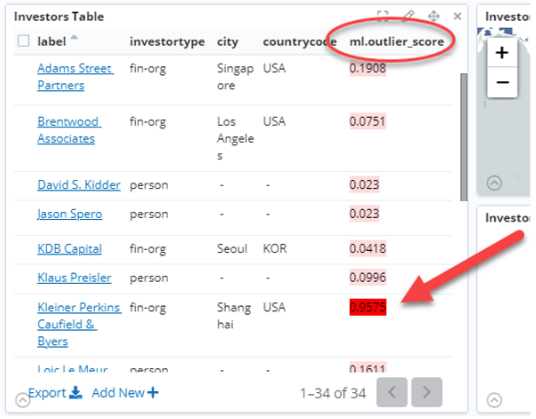
The outlier score appears as an extra field in the target records, which can be used to sort records or to display a color coding scheme. Analysts can view details about how the anomaly score is composed. For example, it may indicate ‘an unusually high number of investments’.
Feature preview: Image and video processing
As we all know, the incredible amount of media generated by the digitized society we live in can no longer be covered by human analysis.
We’re working on a standard component to process images and media by using deep learning analysis; created specifically to address the need of investigative use cases.
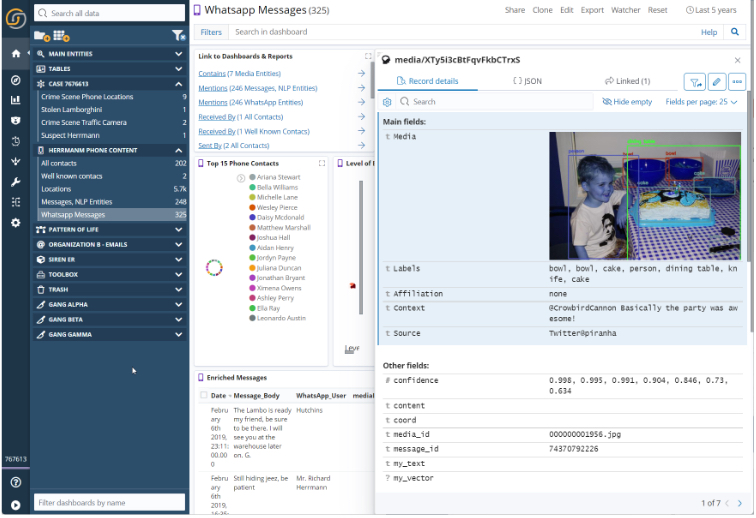
This toolkit provides out-of-the-box capabilities, which include:
- Object and person tagging
- Face vector extraction and search
- Ability to train the tool for custom object categories (such as guns, drugs, etc.)
- Image similarity search based on smart deep learning extracted vectors
- Text-in-image search (such as license plates, addresses, and names)
- General image category detection
Our roadmap items include:
- Audio transcript from videos
- Audio event extraction
- Integration with third-party curated datasets that are law enforcement- and intelligence-specific
Part of this can be seen in action in this video about our search functionality: Investigative grade “search” in the Siren Platform
NOTE: This feature is not yet part of the product, but we are making it available as part of selected engagements.
Wrapping up
Siren’s mission is to protect people, assets and networks with a uniquely fresh and self-managed approach to investigative analytics.
We believe that Siren Platform version 12 is a huge step in this direction. It delivers integration of enterprise-wide investigative Search with analytics, while also having the ability to create graphs and tell a story.
Customers previously used expensive legacy software just as a graph drawing board, which was disconnected from any “big data search” and was far from being easily managed by the organizations. Not anymore…
Here are some resources to get you started:



